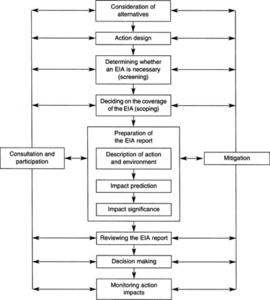
The process of conducting an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report for a gas power plant is crucial in ensuring that the project is undertaken in an environmentally responsible and sustainable manner.
In today’s energy-hungry world, the demand for power generation is ever-increasing. Gas power plants have emerged as a significant player in meeting this demand due to their efficiency and relatively lower carbon emissions compared to coal-fired power plants or diesel power plants. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and it is essential to evaluate the environmental impact of gas power plants to strike a balance between energy needs and sustainability.
In this blog, we will take a closer look at the steps involved in carrying out an EIA study for a gas power plant and the key considerations that need to be taken into account.
Step 1: Scoping
The first step in preparing an EIA report is to scope the project. This involves identifying the key environmental issues that are likely to be impacted by the project, as well as any potential social or economic impacts. For a gas power plant, some of the key issues may include air and water pollution, noise pollution, and land use changes. The scoping process involves consultation with stakeholders, including the local community, government agencies, and environmental groups, to identify their concerns and priorities.
Step 2: Baseline Data Collection
Once the scope of the EIA report has been established, the next step is to collect baseline data on the environment and social and economic conditions in the project area. This includes data on air and water quality, soil conditions, biodiversity, cultural heritage, and social and economic conditions. This data is used to establish a baseline against which the impacts of the project can be assessed.
Step 3: Impact Assessment
The impact assessment stage involves identifying the potential impacts of the project on the environment and social and economic conditions in the project area. For a gas power plant, this may include emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants, impacts on local water resources, and changes to land use patterns. The impact assessment considers both the direct impacts of the project, as well as any cumulative or indirect impacts that may arise as a result of the project.
Step 4: Mitigation Measures
Based on the findings of the impact assessment, the next step is to identify and evaluate potential mitigation measures that can be put in place to reduce or eliminate the negative impacts of the project. This may include measures such as the use of pollution control technologies, water conservation measures, and measures to minimize noise pollution. The effectiveness of these measures is evaluated in terms of their ability to reduce or eliminate the identified impacts.
Public Consultation: Involving the public and stakeholders in the decision-making process. Their input helps address concerns and ensures transparency in the project’s development.
Step 5: Monitoring and Management
The final step in the EIA process is to develop a monitoring and management plan to ensure that the mitigation measures are implemented effectively and that the project is managed in a sustainable manner. This plan includes monitoring the implementation of the mitigation measures, as well as monitoring the environmental and social impacts of the project over time.
In conclusion, the preparation of an EIA report for a gas power plant involves a comprehensive and systematic process of scoping, baseline data collection, impact assessment, and the development of mitigation measures and monitoring plans. This process ensures that the project is undertaken in an environmentally responsible and sustainable manner, taking into account the concerns and priorities of stakeholders and the potential impacts on the environment and social and economic conditions in the project area.